Mitsubishi Materials Corporation (TSE: 5711): Stock Analysis
August 3, 2025
1. Introduction
Mitsubishi Materials Corporation (MMC) is one of Japan’s largest diversified materials manufacturers, with a focus on copper smelting, advanced materials, and precision tools. The company plays a critical role in the global supply chain for semiconductors, EVs, and renewable energy infrastructure. Leveraging its expertise in circular economy practices and material science, MMC aims to become a sustainability-driven growth company under its “Mid-Term Strategy 2030.”
2. Stock Price Development
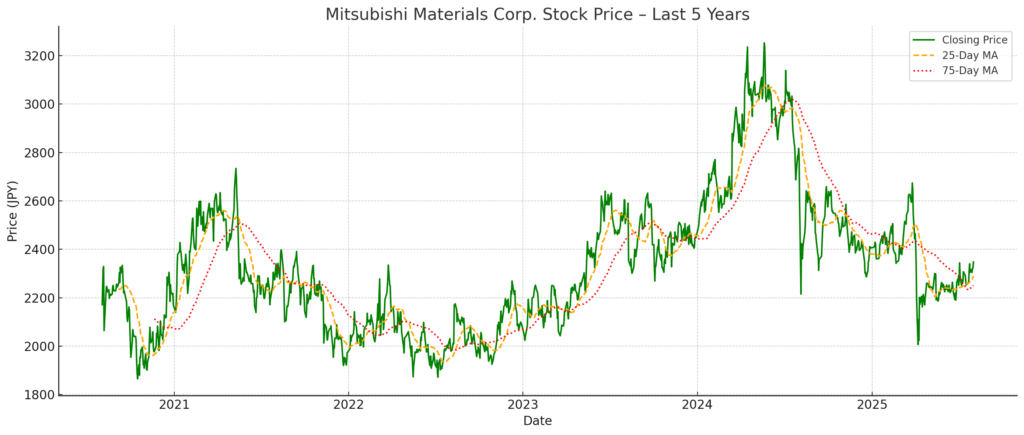
Between 2020 and 2024, Mitsubishi Materials Corporation’s stock exhibited modest volatility and a mixed performance, reflecting macroeconomic factors, business restructuring, and shifting investor expectations. The year-end closing prices are summarized below:
| Fiscal Year | Year-End Closing Price (JPY) | Annual Change (%) | Key Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 2,170.0 | — | Recovery from pandemic-driven lows |
| 2021 | 1,975.0 | ▲9.0% | Decline in ROE, weak operating cash flow |
| 2022 | 2,084.0 | +5.5% | Structural reform including cement spin-off |
| 2023 | 2,447.5 | +17.4% | Strong earnings recovery, especially in processing tools |
| 2024 | 2,405.5 | ▲1.7% | Slower EPS growth despite revenue rebound |
Key Observations:
2021 marked a retreat, driven by declining return on equity (ROE fell from 4.6% to 3.5%) and a sharp drop in operating cash flow. Market sentiment reflected doubts over capital efficiency and the sustainability of earnings.
2022 saw a moderate rebound, bolstered by the divestiture of the cement business (transferred to UBE Mitsubishi Cement), leading to a leaner operating structure and more focused capital allocation.
2023 witnessed a strong rally, with the stock surging 17.4% amid improved profitability in the processing and high-performance product segments. The operating cash flow rose to ¥45.2 billion, and investor confidence improved with a higher equity ratio (31.4%).
2024 experienced mild correction, as investors digested the early outcomes of the Mid-Term Strategy 2030. While earnings per share (EPS) and ROE improved (up to 5.1%), the pace of transformation and capital returns remained moderate, leading to a slight retreat in share price.
Trend Interpretation:
The stock has generally responded more to tangible financial improvements—such as cash flow, ROE, and segment profitability—than to long-term strategic announcements alone.
The Mid-Term Strategy 2030, while well-received in narrative, appears to be priced in cautiously. Institutional investors may be waiting for concrete ROIC improvements toward the target level of 9% before re-rating the stock significantly.
The stock’s behavior suggests limited speculative premium, and instead reflects measured valuation tied to near-term execution capability.
3. Financial and Operational Analysis
3.1 Key Financial Metrics (FY2021–FY2025)
| Fiscal Year End | Revenue (bn JPY) | Operating Profit (bn JPY) | Net Profit Attributable to Owners (bn JPY) | ROE (%) | Operating CF (bn JPY) | Equity Ratio (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FY2021 (Mar-21) | 1,485.1 | 26.6 | 24.4 | 4.6 | 125.3 | 26.8 |
| FY2022 (Mar-22) | 1,811.8 | 52.7 | 45.0 | 8.0 | 6.8 | 27.5 |
| FY2023 (Mar-23) | 1,625.9 | 50.0 | 20.3 | 3.5 | 45.2 | 31.4 |
| FY2024 (Mar-24) | 1,540.6 | 23.3 | 29.8 | 4.8 | 51.4 | 30.2 |
| FY2025 (Mar-25) | 1,962.1 | 37.1 | 34.1 | 5.1 | 58.9 | 28.5 |
3.2 Observations
Revenue Trends and Growth Profile
Revenue rebounded sharply in FY2022 (+22.0%) amid rising metal prices and recovery in global manufacturing, particularly in the automotive and semiconductor sectors.
After a dip in FY2023 and FY2024 due to macro headwinds and inventory adjustments, FY2025 revenue surged to a record ¥1.96 trillion (+27.4% YoY), supported by strong demand in precision tools and copper products.
Profitability and Capital Efficiency
Net profit remained volatile, reflecting fluctuations in metal prices and structural transformation costs.
ROE stayed below 6% throughout the period, underscoring concerns around capital productivity and margin scalability.
Cash Flow and Financial Health
Operating cash flow showed a U-shaped recovery: peaking in FY2021 due to inventory compression, troughing in FY2022 due to working capital outflow, and steadily improving through FY2025.
Despite high capex related to strategic investment (LIB recycling, precision tools, geothermal), the equity ratio remained stable near 30%, indicating prudent leverage usage.
Segment Performance (FY2025)
Processing Business (Precision Tools): Highest growth contributor, driven by global expansion and integration of H.C. Starck (Europe).
Metal Business (Copper, Gold, Silver): Stable margin generator, but sensitive to commodity cycles.
High-Performance Products: Benefited from semiconductor demand; increased investment in heat-resistant alloys and functional ceramics.
Renewable Energy: A small but growing segment with geothermal power as a core focus.
Cement Business: Fully separated since FY2022 (UBE Mitsubishi Cement), improving capital allocation efficiency.
Operational Highlights
CAPEX Strategy: Over ¥100 billion cumulative investment across FY2023–FY2025 in high-margin and ESG-linked businesses.
Efficiency Challenge: Despite higher earnings, ROIC remained below the company’s 9% target, reflecting the capital-intensive nature of its transformation.
Management Incentives: Executive compensation partially tied to financial KPIs (Net Profit, Operating Profit) and non-financial benchmarks (competitor comparisons, ESG progress).
4. Valuation
As of August 1, 2025, Mitsubishi Materials Corporation (MMC) trades at notably low valuation multiples, despite reporting record earnings in FY2025. This disconnect reflects investor caution around capital efficiency and the pace of strategic transformation.
Key Valuation Metrics:
| Metric | Value | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| Share Price | ¥2,347.5 | As of August 1, 2025 |
| EPS (FY2025) | ¥260.82 | Strong recovery from prior years |
| PER | ~9.0x | Well below sector averages (12–15x) |
| BPS | ¥5,183.34 | Indicates solid net asset position |
| PBR | ~0.45x | Reflects deep discount to book value |
| Dividend Yield | ~2.4% | Based on stable DPS of ¥56–58 |
| ROE | 5.1% | Still below estimated cost of equity (7–8%) |
Observation:
The current Price-to-Earnings Ratio (~9.0x) suggests that the market is not fully pricing in MMC’s earnings recovery, possibly due to lingering concerns over return on invested capital.
A Price-to-Book Ratio of 0.45x is exceptionally low, especially given MMC’s stable balance sheet and improving profitability. This implies that investors are skeptical about the company’s ability to generate shareholder value from its assets.
While earnings and cash flow have improved, the company’s ROIC remains below WACC, delaying any valuation multiple expansion.
The market appears to assign little value to emerging businesses such as LIB recycling and geothermal power, which could act as valuation catalysts if monetization progresses.
5. Strategic and Technological Positioning
Mitsubishi Materials Corporation (MMC) is executing a multi-year transformation under its “Mid-Term Strategy 2030,” aiming to evolve from a traditional materials producer into a sustainability-driven, technology-enabled enterprise. The strategy is built upon three pillars:
5.1 Strategic Pillars
(1) Circular Economy and Resource Recycling Leadership
MMC is positioning itself as a global leader in non-ferrous metal recycling, focusing on electric vehicle batteries (lithium-ion) and electronics.
The company is expanding its Urban Mining Center network, integrating collection, refining, and metal extraction.
A new LIB (Lithium-Ion Battery) recycling plant in Europe is under construction, leveraging MMC’s expertise in copper, nickel, and cobalt recovery.
Strategic Goal: Achieve a 20% share of global LIB recycling market by 2030 .
(2) High-Performance Materials for Next-Gen Industries
Strong investment in materials supporting semiconductors, EVs, and energy systems:
Heat-resistant copper alloys, ceramic substrates, and bonding wires.
Functional coatings for power devices and automotive electronics.
Strategic alliances and M&A (e.g., H.C. Starck) have expanded MMC’s European footprint in advanced materials and powder metallurgy.
Focus Industries: EVs, 5G, aerospace, and high-performance computing.
(3) Carbon Neutrality and Renewable Energy Development
Targeting carbon neutrality by 2045, MMC is scaling up its geothermal, hydroelectric, and solar businesses.
Currently, geothermal power accounts for ~60% of its renewable output.
Strategic investment is directed toward binary power generation and joint development with local governments in Japan and Southeast Asia.
ESG Target: 50% of power consumption from renewables by 2030 .
5.2 Technological Differentiators
| Area | Technology / Capability | Strategic Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Recycling | Advanced hydrometallurgy, closed-loop smelting | Competitive recovery efficiency for LIBs and e-waste |
| High-Performance Materials | Ultra-fine powder metallurgy, precision sintering | Application in EV motors, aerospace, semiconductors |
| Energy | Deep geothermal drilling, binary cycle generation | Strong IP base, government partnerships |
MMC maintains over 2,000 registered patents globally, and invests over ¥10 billion annually in R&D, with 35% allocated to green transformation projects .
5.3 Organizational and Capital Structure Reform
The cement business divestiture in 2022 (UBE Mitsubishi Cement) improved strategic focus and capital allocation.
Business units were reorganized into core growth (materials, recycling) and stable cash-flow (metals, tools) clusters.
MMC has also restructured its internal governance, linking executive KPIs to strategic metrics (e.g., ROIC, ESG scores, peer benchmarking).
5.4 Outlook
MMC’s strategic positioning provides it with:
A defensive base in copper smelting and tools,
A growth engine in green technologies,
A differentiated ESG profile among Japanese industrials.
However, execution risk remains in scaling recycling and energy businesses while achieving meaningful capital returns.
6. Risks and Catalysts
Mitsubishi Materials Corporation (MMC) operates across capital-intensive, globally exposed industries, ranging from metal smelting to high-performance materials and renewable energy. As such, the company faces a complex matrix of risks and opportunities. Below, we categorize the key external and internal drivers that may influence MMC’s performance and valuation trajectory in the coming years.
6.1 Catalysts
| Catalyst | Description | Impact Horizon | Strategic Implication |
|---|---|---|---|
| EV and Battery Recycling Expansion | Demand for lithium-ion battery (LIB) recycling is accelerating due to global EV adoption. MMC’s proprietary smelting and hydrometallurgical technology positions it to become a leader in this space. | Mid to Long Term | Drives growth and ESG valuation premium |
| Semiconductor Supply Chain Localization | Governments and OEMs are pushing for resilient, domestic supply chains for critical materials. MMC’s copper alloys and thermal materials are vital components. | Short to Mid Term | Boosts high-margin product demand |
| Geothermal Power Scaling | Japan’s green energy transition is accelerating. MMC is one of few players with operational know-how and license holdings in geothermal power. | Long Term | Reinforces ESG differentiation and energy diversification |
| Portfolio Restructuring Completed | The cement divestiture and reorganization of business units allow for more focused capital deployment and operational efficiency. | Immediate | Improves capital productivity and ROIC outlook |
| ROIC Target of 9% by FY2030 | If achieved, this could justify a re-rating in MMC’s valuation multiples from current ~0.45x PBR and ~9.0x PER. | Mid Term | Increases attractiveness to institutional investors |
6.2 Risks
| Risk | Description | Severity / Horizon | Mitigation Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| Commodity Price Volatility | MMC’s earnings are sensitive to copper, gold, silver, and rare metal prices. Margin compression during down cycles can affect profitability. | High / Short Term | Hedging partially implemented; structural exposure remains |
| Execution Risk in Strategy 2030 | Capital investments in LIB recycling, geothermal, and advanced materials are sizable. Any delays, budget overruns, or demand shortfalls could weigh on returns. | Medium to High / Mid Term | Governance improvements and KPI alignment in place |
| Low Capital Efficiency (ROE/ROIC) | Despite stable cash flows, historical returns on invested capital remain under cost of capital (~5–6%), leading to undervaluation. | Medium / Persistent | ROIC initiatives underway, but results not yet visible |
| Geopolitical Risk (Indonesia, Europe) | MMC holds major assets in politically sensitive countries such as Indonesia (mining) and is expanding in Europe (LIB recycling). | Medium / Mid Term | Country risk is acknowledged but not yet diversified |
| Regulatory and ESG Scrutiny | The metals and energy sectors face increasing environmental regulation and carbon pricing risks. | Medium / Long Term | MMC is proactively investing in ESG initiatives, but exposure persists |
Summary Table
| Category | High Impact Catalysts | Key Risks |
|---|---|---|
| Short Term | Semiconductor demand surge | Metal price volatility |
| Mid Term | LIB recycling, ROIC improvement | Execution risk in green tech investment |
| Long Term | Geothermal power growth, ESG leadership | Regulatory shifts, geopolitical exposure |
MMC’s ability to convert structural ESG tailwinds into shareholder value depends on its operational execution, capital discipline, and communication with the capital markets. The valuation multiple compression over the past years is a reflection of these uncertainties, but the company now has the building blocks in place to reestablish investor trust.
7. Conclusion
Mitsubishi Materials Corporation (MMC) stands at a pivotal juncture in its long-term corporate transformation. Over the past five years, the company has made deliberate progress in redefining its portfolio—from a traditional non-ferrous and cement conglomerate into a focused, ESG-oriented materials innovator.
From a financial standpoint, MMC has demonstrated improving fundamentals:
Revenue reached an all-time high of ¥1.96 trillion in FY2025.
Operating cash flow grew steadily, while equity ratio remained conservative (~28.5%).
The ROE recovery to 5.1% marks progress, though it still lags global peers.
Strategically, the company’s execution of the Mid-Term Strategy 2030 has created a compelling narrative centered around:
LIB recycling and circular economy leadership
High-performance materials for EVs, 5G, and semiconductors
Geothermal energy expansion and carbon neutrality
Yet, challenges persist. Despite improved fundamentals, valuation metrics (PBR ~0.45x, PER ~9.0x) indicate that the market continues to apply a significant discount. This reflects persistent concerns over capital efficiency—particularly the gap between ROIC and the estimated WACC of 5–6%. Investors are likely awaiting stronger evidence of execution on MMC’s mid-term growth strategies. In addition, exposure to commodity price fluctuations and geopolitical uncertainties requires active risk mitigation.
That said, MMC offers a unique asymmetric opportunity:
Downside is limited by a defensive metals/tool business and clean balance sheet.
Upside is substantial if it delivers on its sustainability-linked roadmap and achieves ROIC ≥9% by 2030.
For long-term, ESG-conscious investors—particularly those seeking industrial exposure to the green transition—MMC provides both strategic optionality and re-rating potential.
At Wasabi Info, we publish concise equity reports and market insights through our blog—
but our core value lies in providing bespoke, on-demand research for international clients.
Whether you are a private investor or a corporation, we deliver confidential, tailored intelligence designed to support strategic decisions.
Our research services include:
• Equities: In-depth analysis of Japan-listed companies not featured in the blog
• Competitor Analysis: Detailed mapping of industry rivals and market dynamics
• Market Entry Intelligence: Insights into local barriers, regulations, and competitor positioning
• Real Estate & Assets: Localized assessments for factory, hotel, or retail expansion
• Field Intelligence: On-the-ground surveys and discreet market checks unavailable through public sources
Reports are available in English, Chinese, and Japanese.
For inquiries, please contact: admin@wasabi-info.com
© Wasabi Info | Privacy Policy
Disclaimer
This report is intended for informational purposes only and does not constitute investment advice. The analysis contains forward-looking statements and interpretations based on publicly available information as of the date of writing. Readers should conduct their own research and consult with a licensed financial advisor before making any investment decisions.
Wasabi-Info.com shall not be held liable for any loss or damage arising from the use of this report or reliance on its contents.